INSTRUCTIONS ON HOW TO ANALYZE REGULATING VARIABLES IN CB SEM MODEL USING AMOS
♠ To better understand moderating variables, you can refer to Moderation page 361, book number 2 on the topic of statistical analysis published by Oxford University in 2013. Authors Marsh, H. W., Hau, K. T. , Wen, Z., Nagengast, B., and Morin gave details about the impact of moderator variables in the causal model. For example, to determine whether the cause-and-effect relationship between Brand Loyalty and Repeat Purchase Intention is influenced by Gender? And specifically how does it affect this relationship? Gender now acts as a moderating variable that directly affects the linear relationship between Brand Loyalty and Repeat Purchase Intention.
♠ To evaluate the moderator variable we need to go through the INT variable, INT variable = Gioi_tinh*LY. Consider the influence of INT and conclude about moderating variables. Specifically:
INT = Interation (Interaction)
The research model is as follows:

Including the moderator variable INT (INT = LY*Gender) into the research model, remember to include the Gender variable as well.
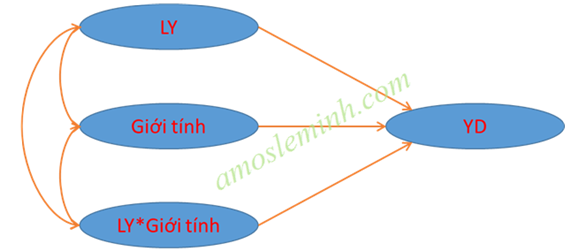
The moderator variable analysis model is as follows:
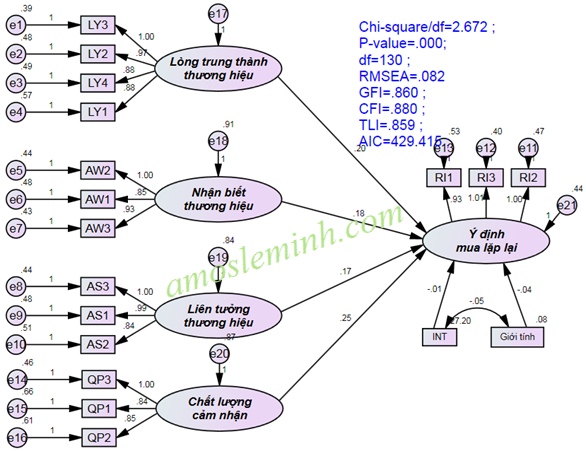
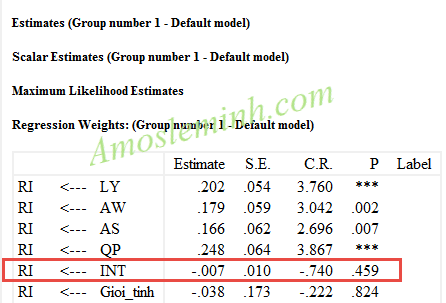
The results of P-value analysis show that INT does not have a significant influence on RI (Repeat Purchase Intention). Therefore, it is concluded that Gender does not influence the cause and effect relationship between LY and RI.
If you need help during the implementation process, please contact Le Minh’s Data Processing and Analysis Service! Thank you very much!






